Why Stock Splits Matter To Investors
Stock splits are a common event in the world of investing, yet they are often misunderstood or underestimated in their importance. While they don't directly impact the value of an investor's holdings in a company, stock splits can significantly influence investor perception, market behaviour, and a company's ability to maintain its growth trajectory. Understanding why stock splits matter to investors requires a deeper look into the mechanics behind them, the potential benefits they offer, and how they can shape market dynamics.
What Is A Stock Split?
A stock split is a corporate action that increases the number of a company's outstanding shares while proportionally reducing the price per share. For example, in a 2-for-1 stock split, shareholders receive two shares for every share they already own, but the price per share is halved. If the stock were previously priced at $100 per share, after the split, each share would be worth $50, but the investor would own twice as many shares. Importantly, this does not change the overall value of the investment. The total value of the shares remains the same, as the increase in the number of shares is offset by the lower price per share.
Why Stock Splits Matter: Impact On Liquidity
One of the primary reasons stock splits matter to investors is that they improve liquidity in the market. Liquidity refers to how easily assets, such as stocks, can be bought or sold without affecting the price significantly. When the stock price becomes very high, fewer investors may be able to afford to purchase shares, especially smaller investors or those with limited capital. By splitting the stock, the company lowers the price per share, which in turn can attract a wider range of potential buyers.

This increase in liquidity can be beneficial for investors, as it makes it easier to enter or exit positions in the stock. A more liquid market allows for faster transactions and may reduce the potential for significant price fluctuations when large orders are placed. Liquidity also enhances the stock’s ability to be traded more efficiently, which can be especially important for institutional investors who need to execute large orders without disrupting the market.
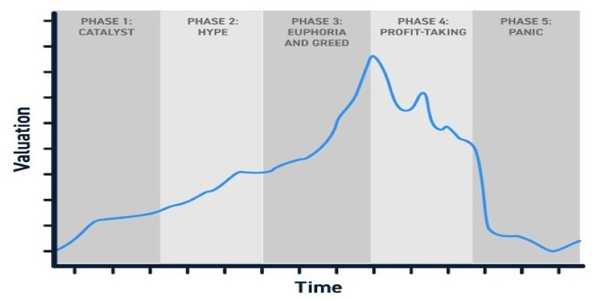
Impact On Volatility And Stock Performance
Stock splits can also affect the volatility and performance of a stock. After a split, the price per share is generally lower, which can make the stock less volatile in the short term. This is because smaller price movements, in percentage terms, may seem less dramatic when the stock price is lower. For example, a 10% move in a stock priced at $1,000 is much larger in absolute terms than a 10% move in a stock priced at $100.
However, the long-term impact of stock splits on volatility is less clear. While some studies suggest that stock splits can lead to increased trading volume and higher stock prices in the short term, the effects on long-term volatility and performance vary depending on the company and market conditions. In some cases, the stock price may continue to rise after the split as a result of increased demand. In contrast, in other cases, the stock may experience volatility as investors reassess the company's prospects.
Signaling Growth And Confidence
A stock split can also be seen as a signal of growth and confidence from a company’s management. Often, companies that announce stock splits have been performing well and have seen their stock prices rise significantly. The decision to split the stock is typically made when the company is confident in its future growth prospects and wants to make its shares more attractive to investors.

Investors may interpret a stock split as a sign that the company is in good financial health and expects to continue growing. This positive signal can help boost investor confidence, which in turn can drive the stock price higher. Additionally, a company that is able to split its stock consistently may be seen as having a strong track record of growth, which can enhance its reputation among investors.
The Risks Of Stock Splits
While stock splits may seem like a positive development for investors, they do come with certain risks. One potential risk is the possibility that the company’s stock price may not continue to rise after the split. In some cases, the increased liquidity and investor demand following a stock split may not be enough to sustain the stock price over the long term. If the company’s fundamentals do not support the higher stock price, the stock may experience a decline.

Another risk is the potential for dilution. While stock splits do not directly dilute the value of an investor’s holdings, they do increase the total number of shares outstanding. This can have a dilutive effect on earnings per share (EPS) and may affect the company’s valuation. Investors should carefully consider the potential impact of dilution on their investment before deciding to buy or sell shares following a stock split.
How Stock Splits Affect Dividend Payments
In addition to their impact on stock prices and liquidity, stock splits can also affect dividend payments. Companies that pay dividends typically adjust their dividend payouts after a stock split to reflect the increase in the number of shares outstanding. For example, if a company pays a $2 dividend per share and announces a 2-for-1 stock split, the dividend per share would be reduced to $1 per share, but shareholders would now receive twice as many shares.

While this adjustment keeps the total dividend payout the same, it can affect the perceived value of the dividend for investors. Some investors may be disappointed by the reduction in the dividend per share, even though the total value of the dividend remains unchanged. On the other hand, the increased number of shares may result in higher overall dividend income for shareholders who own more shares after the split.
Conclusion:
Stock splits matter to investors because they can influence liquidity, market perception, and the overall dynamics of a company’s stock. While stock splits do not directly change the underlying value of a company or the total value of an investor’s holdings, they can have a significant impact on how a stock is perceived and traded in the market. Increased liquidity, improved accessibility, and the positive psychological effects of a stock split can drive demand for shares, which may lead to higher stock prices in the short term.